The Secret Nighttime World of Fledgling Birds
Bird enthusiasts and nature lovers alike often find themselves captivated by the mysterious lives of our feathered friends. One question that frequently arises is where fledglings – young birds that have just left the nest – sleep at night. In this post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of fledgling birds, discussing their sleeping habits, the factors that influence where they rest, and how we can help ensure their safety during these vulnerable early days.

Quick Answer:
Where do Fledglings Sleep at Night?
Fledglings sleep at various locations depending on their species and environmental factors. Ground-dwelling species sleep close to the ground in dense vegetation, tree-dwelling species sleep on branches or in the canopy, and cavity-nesting species sleep inside cavities in trees, rocks, or artificial nest boxes.
Developmental Stages of Fledglings
Before we dive into the specifics of where fledglings sleep, it’s important to understand what exactly a fledgling is and how these young birds progress through their early developmental stages.
Fledglings are juvenile birds that have recently left the nest but are still dependent on their parents for food and guidance. This period of time varies among species, lasting from a few days to several weeks. During this stage, fledglings develop their flight skills, learn to find food, and become more independent.
There are several key developmental stages that fledglings go through as they grow and mature. Each stage has its own unique sleeping habits and requirements:
Nestling stage: These are the youngest birds, typically unable to leave the nest. At this stage, they rely entirely on their parents for warmth, food, and protection. Nestlings sleep inside the nest, often nestled against their siblings for additional warmth.
Branching stage: As fledglings become more mobile, they start to explore the area immediately surrounding their nest, often hopping or flitting between branches. At this stage, they may sleep on branches close to the nest, returning to the safety of the nest if necessary.
Fledgling stage: Once they’ve developed their flight skills and can follow their parents, fledglings start to venture further from the nest. At this point, they’ll sleep in various locations that provide shelter and protection, depending on their species and environmental factors.
Fledgling Sleeping Locations
The specific sleeping locations for fledglings vary depending on their species, as well as the environment they inhabit. Broadly, we can categorize bird species into three groups based on their nesting habits: ground-dwelling, tree-dwelling, and cavity-nesting species.
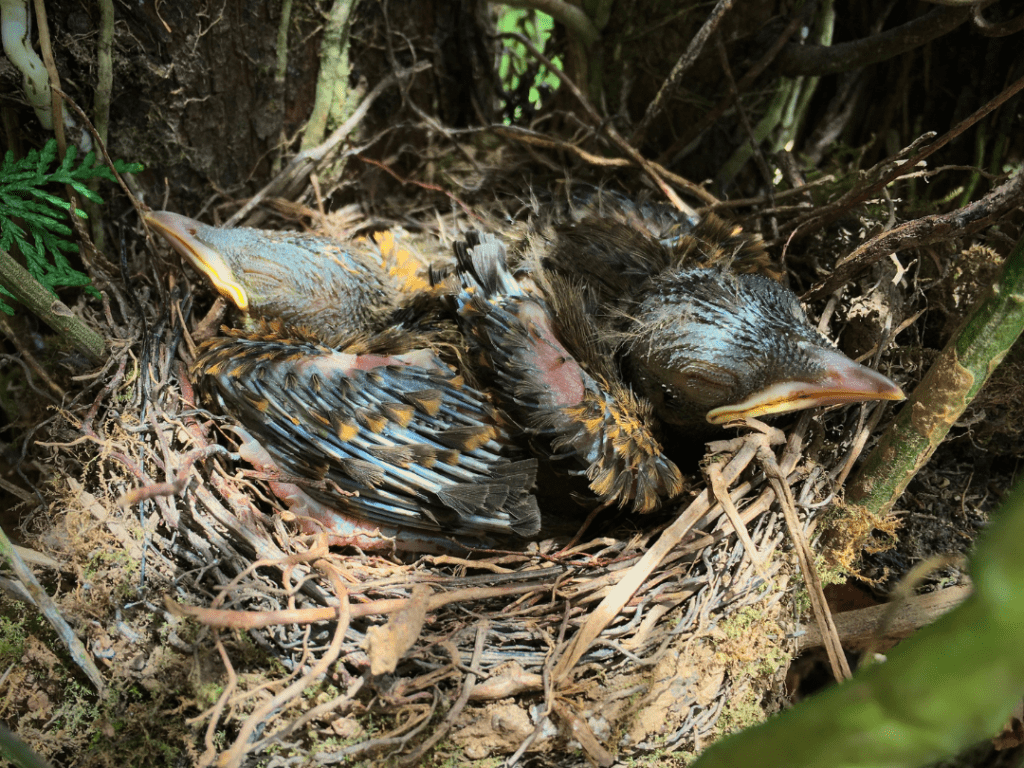

Ground-dwelling species
These birds typically build their nests on the ground, hidden among shrubs or tall grass. Examples of ground-dwelling species include quails, pheasants, and some sparrows. As fledglings, they will sleep close to the ground, seeking shelter in dense vegetation to stay hidden from predators.
Tree-dwelling species
Tree-dwelling birds, such as robins, orioles, and many songbirds, build their nests on tree branches or in the tree canopy. Fledglings of these species will often sleep on branches, clinging to the bark or nestled among leaves for protection from the elements and predators. In some cases, they may return to their nest or another nest-like structure for added security.
Cavity-nesting species
Birds like woodpeckers, owls, and some swallows build their nests in natural cavities found in trees or rocky outcrops. These species may also take advantage of artificial nest boxes provided by humans. Fledglings from cavity-nesting species will sleep either inside these cavities or in similar sheltered locations, such as crevices in tree bark or among rocks.
Factors Influencing Fledgling Sleep Habits
There are several factors that can influence where and how fledglings sleep at night. These include environmental conditions, predator presence, and the guidance of their parents.
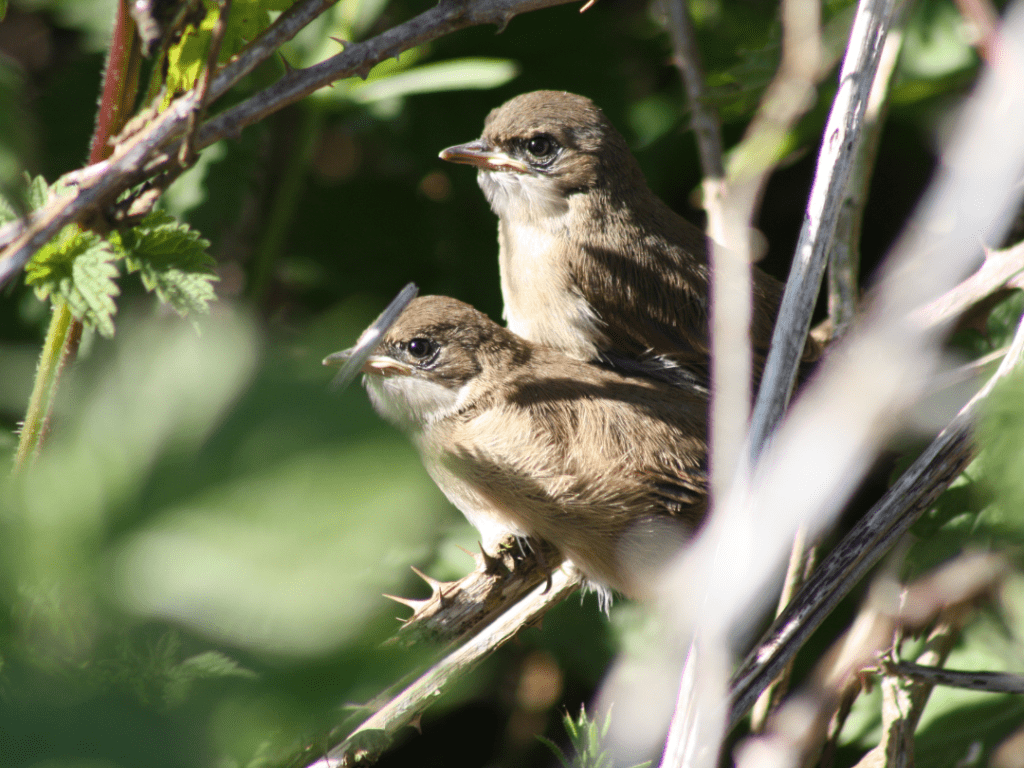
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, such as weather conditions and availability of shelter, can greatly impact where fledglings choose to sleep. In extreme heat, cold, or during heavy rain, fledglings may seek out more protected locations to stay dry and maintain their body temperature. Dense vegetation, tree cavities, or even human-made structures may provide the necessary shelter during harsh weather conditions.
Predator presence
Predators, such as larger birds, snakes, and mammals, pose a significant threat to fledglings. As a result, young birds will seek out sleeping locations that offer protection and camouflage from these potential threats. Fledglings may select spots that are difficult for predators to access, such as high up in trees, hidden among dense foliage, or in tight crevices. Additionally, some species may use a strategy called “roosting,” where they huddle together with other birds of the same species for added protection and warmth.
Parental guidance
The role of parent birds in determining sleeping locations for fledglings should not be overlooked. Parents will often guide their young to suitable sleeping spots and may continue to keep watch over them throughout the night. In some cases, parent birds may even share the sleeping location with their fledglings, providing added warmth and protection.
Promoting Safe Sleep for Fledglings
As bird enthusiasts, we can play a part in ensuring the safety of fledglings during their early days outside the nest. By creating bird-friendly habitats and reducing threats, we can help young birds thrive and grow into healthy adults.
Creating bird-friendly habitats
One of the most effective ways to promote safe sleep for fledglings is to create a bird-friendly habitat in your own backyard or community. This can be achieved by:
Planting native vegetation: Native plants provide natural shelter and food sources for birds. Choose a variety of plants, including trees, shrubs, and grasses, to create a diverse habitat that caters to the needs of different bird species.
Providing shelter: In addition to plants, consider adding birdhouses, nesting boxes, and roosting boxes to your yard. These structures can provide safe and secure sleeping locations for birds, particularly cavity-nesting species.
Reducing threats
Another crucial aspect of promoting safe sleep for fledglings is to minimize the threats they face. Some steps you can take include:
Keeping pets indoors: Cats and dogs can pose a significant threat to fledglings. By keeping your pets indoors, especially at night, you can reduce the risk to young birds in your yard.
Avoiding the use of pesticides: Pesticides can harm birds directly or indirectly by reducing their food sources. Opt for organic gardening methods or choose bird-friendly alternatives to keep your yard safe for fledglings.
Conclusion
Understanding where fledglings sleep at night and the factors that influence their sleeping habits is not only fascinating but also important for those who wish to promote the well-being of these young birds. By creating bird-friendly habitats and reducing threats, we can help ensure the safety and success of fledglings as they navigate the early stages of their lives outside the nest. So, let’s continue to marvel at the secret nighttime world of fledgling birds and do our part to support their journey towards adulthood.

James has always been an avid outdoorsman. Since a kid, he kept a journal of all the different birds and species he saw. Now he wants to share his passion with other birders with Happy Birding!
